In the automotive electrical system, cables, as the “blood vessels” for electrical energy and signal transmission, their reliability is directly related to the safety and performance of road vehicles. Automotive cables face various mechanical stresses in the complex in-vehicle environment, among which abrasion is a common failure inducer. The sandpaper abrasion test, as a core method to evaluate the abrasion resistance of automotive cables, is of great significance to ensure the stable operation of wires throughout their life cycle.
1. Test Principle and Equipment: Simulating Real Abrasion Scenarios
The sandpaper abrasion test for automotive wires mainly uses sandpaper abrasion to simulate the working condition where cables rub against surrounding components (such as sheet metal, plastic parts, etc.) during vehicle operation.
- Sandpaper type: Depending on test standards and requirements, sandpapers of different materials and grits are used. For example, 180Jaluminum oxide ( Al2O3) sandpaper or 150J garnet sandpaper are commonly used. The abrasive hardness and grit of different sandpapers determine the abrasion intensity.
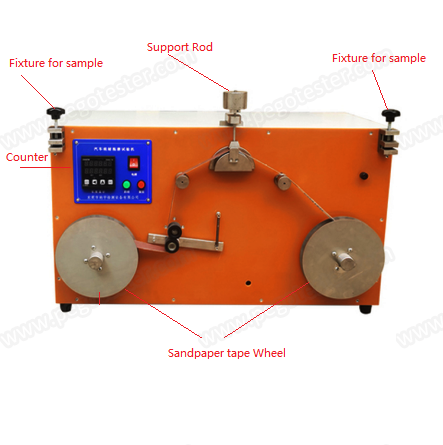
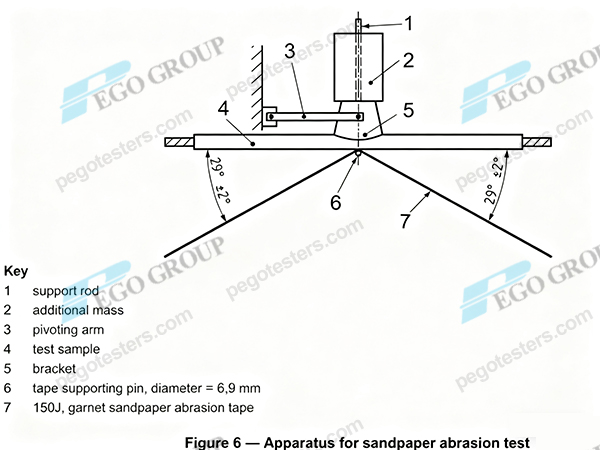
- Test Apparatus: the sandpaper abrasion test apparatus consists of pivoting arm, bracket, loading assembly, sandpaper fixing mechanismand etc.. The apparatus should be able to stably apply a vertical force (usually (0.63±0.05) N) and control the test specimen to move relative to the sandpaper at a speed of (1500±75) mm/min.
2. Test Procedure: Standardized Operation Ensures Reliable Results
The sandpaper abrasion test must strictly follow standardized procedures to ensure the repeatability and comparability of test results.
- Specimen Preparation
Select the automotive cable specimen to be tested and ensure its state is consistent with that in actual vehicle installation. If the specimen is a wire with a conductor, set 5 – 10 mm conductive strips on the sandpaper at intervals of no more than 75 mm to monitor the moment when the conductor is exposed.
- Test Parameter Setting
Loading Force: Apply a vertical force of (0.63±0.05) N to the specimen through the combination of the bracket, pivoting arm, support rod, and additional mass. The additional mass should comply with relevant standards, such as ISO6722-1, ISO 19642-2 and relative national standards.
Motion Control: Fix the specimen horizontally on sandpaper and drag the sandpaper under the sample at a speed of (1500±75) mm/min to make them rub against each other.
- Test Cycle and Result Determination
During each test, move the specimen 50 mm and then rotate it 90° clockwise. Repeat this process a total of 4 times. Record the sandpaper abrasion length when the conductor is exposed due to friction each time. Take the average of the 4 results, which is the “abrasion resistance” index of the cable.
3. Test Significance: A Quality Line from R&D to Mass Production
- R&D Phase: Optimize Cable Design
Through the sandpaper abrasion test, engineers can compare the abrasion resistance of cables with different insulation materials and thicknesses, providing data support for the selection and design of automotive cables. For example, if a certain type of wire wears too quickly in the test, engineers can consider replacing it with a more abrasion-resistant insulation material or increasing the insulation thickness.
- Mass Production Phase: Quality Control Tool
Vehicle manufacturers and component suppliers can use the sandpaper abrasion test as a means of incoming inspection or process quality control to ensure that the mass-produced wires meet reliability requirements. This avoids faults such as short circuits and open circuits caused by cable abrasion, and ensures the stable operation of the vehicle electrical system.
With its simulation of real working conditions and the objectivity of test results, the sandpaper abrasion test for automotive cables has become an indispensable test item in the automotive electrical field. It not only provides a quantitative quality benchmark for the design and production of automative cables, but also fundamentally safeguards the safety and reliability of the automotive electrical system, helping the automotive industry move towards higher quality.




